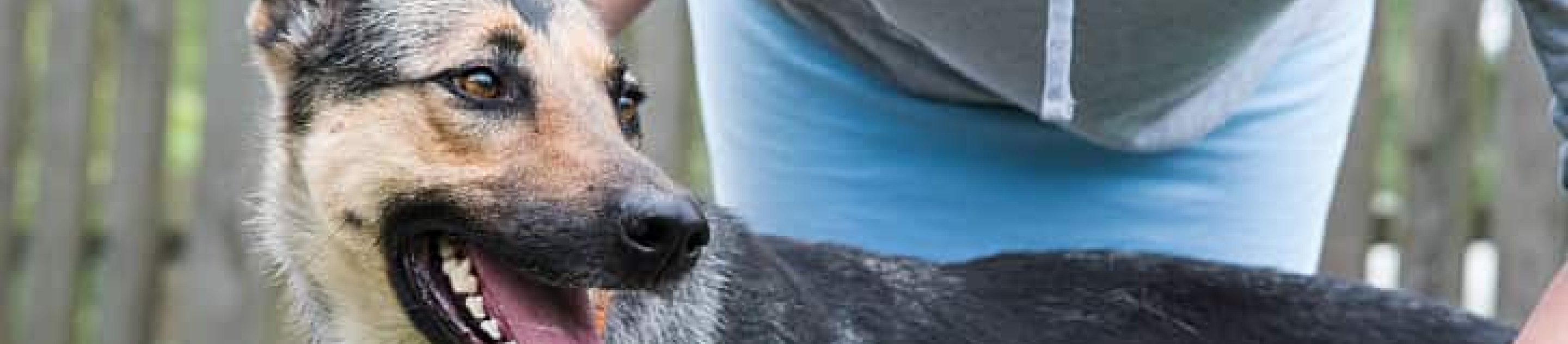
Hair loss in dogs — also known as alopecia — is common and extremely noticeable. Hair loss can appear in a single spot, in patches or all over the body. If you have a dog losing hair at home, you may wonder why and if you need to seek a dog hair loss treatment. There are many things that can cause a dog to lose hair, but it's likely that your pooch is going bald for one of five common reasons.
1. Seasonal Shedding
Sometimes, seemingly extreme dog hair loss is just normal shedding. Dogs lose fur when the individual hairs become old or damaged, or seasonally when the weather turns warm. Many dogs shed year-round. Some breeds, like huskies and Labradors, grow thick winter undercoats that they shed in the spring. Seasonal shedding is often reduced if you live in a moderate climate. If the shedding is out of control, brushing your dog a couple of times a week can remove and control excess hair.
2. Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacteria and yeast are normal inhabitants of canine skin, but sometimes they can grow out of control and create an infection. Bacterial or fungal yeast infections on the skin may cause hair loss, redness, itching and odor. Sometimes, bacterial infections cause pimple-like pustules.
Dogs can also contract ringworm, a fungus that causes hair loss and small areas of infection (no, it's not actually a worm). Red, itchy or scaly patches are cause for a trip to the veterinarian. Your veterinarian will conduct a full examination, recommend some testing and prescribe antibiotics or antifungals to treat the infection if needed.
3. Mange and Other Parasites
Mange is a catch-all term for itchy skin infections caused by mites. Mites are microscopic creatures that live on the surface of the skin or in hair follicles. They cause hair loss and itching by burrowing or chewing on skin. Some mites, like the scabies mite, are extremely contagious to both humans and other dogs, notes the Merck Veterinary Manual. Other mites, like demodex mites, aren't contagious but still cause hair loss and may require treatment.
Fleas are a very common reason for a dog losing hair. Fleas can make dogs itchy to the point of scratching their hair off in places. Mites and fleas are extremely contagious, so any parasites you find on your dog may have already spread to your home and other pets. If you find evidence of mites or fleas, your veterinarian can prescribe an antiparasitic medication and offer tips for ridding your house of pests.
4. Allergies
Dogs can develop allergies just like humans, and some of the most common signs are itchy skin and hair loss. The most common allergies in dogs are environmental allergies to irritants like pollen, mold and dust mites, flea allergies and food allergies. If your veterinarian suspects allergies, they may recommend flea control, medication to control the itching, avoiding allergens or a food change to rule out food allergies.
Food allergies can only be diagnosed by running a food trial for a minimum of eight weeks. If your veterinarian puts your dog on a food trial with a limited-ingredient meal plan or therapeutic food , it is critical to make sure your dog does not eat anything else while on the trial. One treat or stolen bite of chicken can confound the results. If the underlying cause is allergies and they are treated properly, your dog's hair should regrow and the itching should stop.
5. Underlying Medical Conditions
If a dog is losing hair all over their body, then the problem may lie under the hood. The skin is technically the largest organ in the body, and it requires tremendous amounts of nutrients to stay healthy. If your dog has an underlying medical condition, their hair and fur may be affected.
Hormonal conditions — like hypothyroidism, adrenal gland disorders or growth hormone disorders — can all cause a dog to lose hair. If your veterinarian suspects an internal problem as cause for the hair loss, they may recommend laboratory testing and possibly X-rays or ultrasound imaging to determine the cause.
Excessive shedding can be caused by stress, poor nutrition, pregnancy, lactation or an underlying medical condition. If you think your dog is shedding more than normal or if he is developing bald patches, schedule an appointment with your veterinarian. The dog hair loss treatment they prescribe will depend on your pet's other health needs.
A dog losing hair needs to visit the veterinarian, but their condition is often able to be cleared up with a simple change in food or medication. Keep up with regular grooming and brushing so that you can spot the earliest signs of a problem.